Antibody growth and characterization
The immunization and hybridoma era resulted in 53 monoclonal cell traces. The Lachesis sandwich pair was chosen for additional experiments from the antibodies derived from these cell traces. In an oblique sandwich ELISA, the chosen sandwich pair elicited indicators indicative of binding to venom elements from L. muta and L. melanocephala, however not in the direction of Bothrops or Crotalus venoms, indicating that the antibodies have been particular in the direction of their goal (Supplementary Information (SI) Fig. S1). Meanwhile, the chosen Bothrops sandwich pair elicited robust indicators on the venoms from a number of completely different Bothrops species and no sign on venoms from Crotalus or Lachesis species (SI Fig. S1). Therefore, this mAb pair was chosen for software within the LFA because it enabled the precise detection of a lot of the examined Brazilian Bothrops spp. venoms with out cross-reacting with venoms from different medically related snakes within the area.
Evaluation of singleplex LFAs
The Bothrops LFA was examined in 4 clean matrices utilizing working buffers with two completely different surfactants (i.e., Tween-20 or Tergitol) with and with out 4% NaCl. First, borate buffer with 1% BSA and 0.05% Tween-20 was examined as this working buffer has been efficiently utilized in earlier works with CNP-based LFAs with none false positives39,40,41. As may be seen from SI Fig. S2 and SI Table S1, all pattern matrices examined within the NaCl-free working buffers had non-specific binding, leading to false positives; probably the most intense check line was noticed utilizing the working buffer with Tergitol. Adding NaCl to the working buffer lowered the false positives in serum samples, indicating it may inhibit non-specific binding brought on by matrix results, as others have reported31,42. It is crucial to contemplate the supposed pattern matrix early within the LFA growth course of, as success in buffer methods hardly ever displays how the assay will carry out in organic matrices26.
It was vital to incorporate salt within the working buffer to scale back the false positives for the Bothrops LFA. Therefore, buffer optimization experiments for the Lachesis LFA have been carried out with both Tween-20 (SI Fig. S3a) or Tergitol (SI Fig. S3b) and 4% NaCl within the buffer. Despite the presence of NaCl, each clean serum matrices resulted within the look of an intense check line for the Lachesis LFA indicating some matrix impact. In distinction, a false optimistic solely occurred within the plasma matrices examined with the working buffer with Tergitol (SI Fig. S3b). Researchers have reported that testing sera can lead to non-specific binding, presumably as a result of presence of naturally occurring, poly-specific, and low-affinity heterophile antibodies42,43. The pattern matrix (i.e., serum) may require additional dilution within the working buffer to scale back such non-specific binding. The mixture of 4% NaCl and Tween-20 successfully lowered or eradicated the false positives, and subsequently, these elements have been included into the working buffer for additional experiments. The inclusion of salt within the working buffer is a compromise between limiting the false positives and lowering the sign depth on the check and management traces, which may lower the general assay sensitivity.
After optimizing the working buffer, the visible LoDs for the singleplex LFAs have been decided. A focus vary of 1000–1 ng/mL was chosen because it has been reported that it is a clinically related venom vary for the primary 50 h submit viper-bite30. In each singleplex LFAs, there was an obvious lower in check line sign depth with lowering venom focus, with a visible LoD of 10 ng/mL and 50 ng/mL being reached with B. atrox and L. muta venoms respectively (SI Fig. S4).
Comparison of multiplex LFA configurations
Two multiplex LFAs have been developed with completely different check line configurations (i.e., alternating the position of the higher check line between Bothrops and Lachesis) for comparability. In each configurations, the check line intensities and corresponding T/C ratios correlated with the examined venom concentrations.
The visible LoDs of configuration 1 (SI Fig. S5a) in spiked working buffer, have been 10 ng/mL and 100 ng/mL in B. atrox and L. muta venoms, respectively. The sign on the Bothrops line was constantly extra intense than the Lachesis line’s sign, leading to a better B/C in contrast with the L/C worth in any respect examined concentrations. The identical visible LoDs have been reached with configuration 2 (SI Fig. S5b), however a weak sign appeared on the decrease line (Bothrops line) between 10 and 1000 ng/mL in L. muta venom. Moreover, a weak sign additionally developed on the Bothrops line in clean working buffer which was indistinguishable from the sign at 1 ng/mL in B. atrox venom-spiked working buffer. The Bothrops line sign intensities have been comparable between each configurations in B. atrox venom and in each venoms concurrently. However, in configuration 2 the Lachesis line depth (and corresponding L/C worth) was lowered in L. muta venom and in each venoms.
Both configurations have been examined in two clean serum and two clean plasma samples. Weak check line indicators developed within the clean serum matrices in each multiplex configurations (SI Fig. S6), indicating that the matrix impact brought on by serum couldn’t be eradicated by diluting the matrix 10:90 within the working buffer. In distinction, a check line solely developed in clean plasma citrate with configuration 2, demonstrating that this configuration was extra inclined to false positives. As a outcome, configuration 1 was chosen for the remaining experiments.
An important function of multiplexing is distinguishing between or detecting multiple goal in a single pattern. In the bigger focus vary (Fig. 1), the multiplex LFA had visible LoDs of 10 ng/mL for B. atrox (Fig. 1b), 50 ng/mL for L. muta (Fig. 1c), and 50 ng/mL for each venoms (Fig. 1d). However, as a result of each mAb pairs used within the LFA goal particular toxins inside the venoms, not the entire venoms, the precise toxin focus being detected is decrease than reported right here.
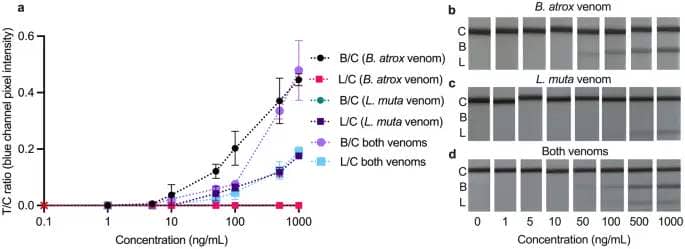
Calibration curves (a) and smartphone pictures (b–d) of the multiplex LFA examined in (b) B. atrox, (c) L. muta, and (d) each venoms, spiked in growing concentrations (1–1000 ng/mL) into the working buffer. Calibration curves plotted as check traces divided by management traces (T/C) ratios (Bothrops/management = B/C; Lachesis/management = L/C) towards venom focus. Error bars symbolize the usual deviation (n = 3), and the crimson cross represents the sign in clean working buffer.
The function of this LFA is to facilitate the differentiation of snakebites brought on by Bothrops and Lachesis which trigger overlapping scientific manifestations in victims, reasonably than to detect the presence of each venoms concurrently, so within the remaining experiments matrices have been solely spiked with a single venom reasonably than a cocktail of each.
Cross-reactivity towards different venoms
The LFA was examined in different related Bothrops, Lachesis, and Crotalus venoms from indigenous Brazilian species. However, it is very important be aware that some Bothrops and Lachesis spp. show ontogenetic and geographic venom variations44,45,46 and the outcomes reported right here relate to the venoms described in SI Table S2. The LFA may detect Bothrops and Lachesis venoms (Fig. 2), apart from B. jararacussu and exhibited a concentration-dependency with constantly darker check traces at 1000 ng/mL in comparison with 100 ng/mL. Still, solely two concentrations have been examined, and the sign intensities have been weak at 100 ng/mL in B. mattogrossensis and B. leucurus venoms indicating the LFA won’t detect these venoms at decrease concentrations. Importantly, no check line sign developed with C. d. terrificus venom at both focus. It could be fascinating to detect C. d. terrificus venom, however this might require a further check line utilizing a mAb pair particular towards Crotalus. Besides, bites brought on by Crotalus end in scientific manifestations which might be distinct from these brought on by Bothrops or Lachesis, making it extra easy to diagnose Crotalus envenoming by classical syndromic approaches5.
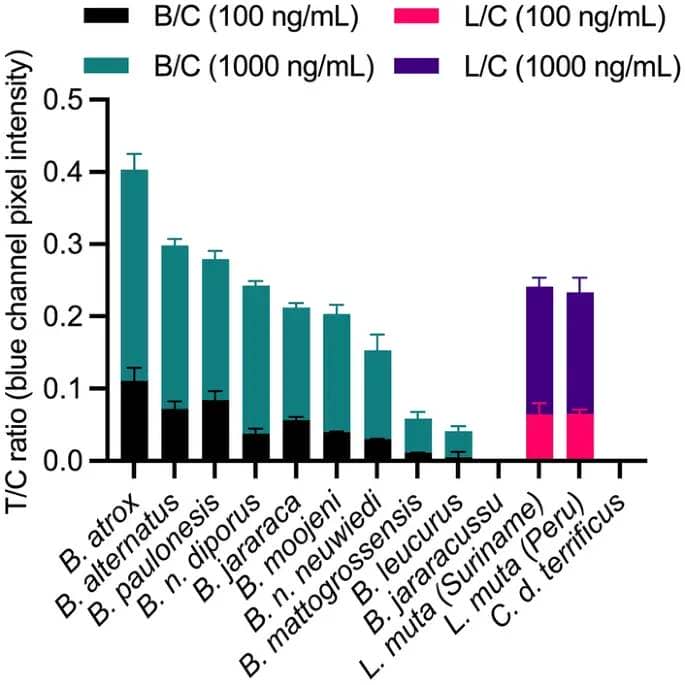
Detection of various goal and non-target venoms spiked into working buffer plotted as check traces divided by management traces (T/C) ratios (Bothrops/management = B/C; Lachesis/management = L/C) towards the completely different venoms at 100 and 1000 ng/mL Error bars symbolize the usual deviation (n = 2).
Evaluation of multiplex LFA in spiked matrices
The LFA was examined in urine and plasma (citrate, heparin, and K2EDTA) matrices spiked with both B. atrox (Fig. 3a, c) or L. muta (Fig. 3b, d) venom. In all examined matrices, the check line intensities (and corresponding B/C and L/C ratios) decreased with lowering venom focus, leading to a relative normal deviation (%RSD) of < 14.5% at concentrations of 100 ng/mL (Table 2).
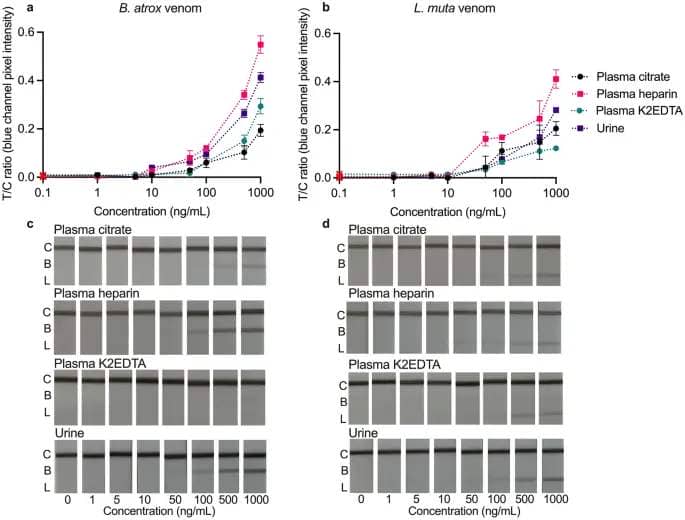
Calibration curves (a, b) and smartphone pictures (c, d) of the multiplex LFA examined in growing concentrations (1–1000 ng/mL) of B. atrox (a, c) or L. muta (b, d) venom spiked into plasma (citrate, heparin, K2EDTA), and urine matrices. Calibration curves are plotted as check traces divided by management traces (T/C) ratios (Bothrops/management = B/C; Lachesis/management = L/C) towards focus. The B/C isn’t proven for the L. muta assessments, and the L/C isn’t proven for the B. atrox assessments, as no indicators developed. Error bars symbolize the usual deviation (n = 3), and the crimson cross represents the sign in a clean working buffer.
Overall, the check traces have been constantly extra intense on the Bothrops line in contrast with the Lachesis line, leading to larger B/C than L/C values (Fig. 3). Plasma samples collected in tubes containing completely different anticoagulants have been assessed as it’s understood that pattern assortment can affect assay sensitivity26. In the plasma matrices, the B. atrox venom resulted in visible LoDs of 10 ng/mL (citrate and heparin) or 50 ng/mL (K2EDTA), whereas L. muta venom constantly gave a LoD of fifty ng/mL. Except for a really weak sign on the Lachesis line in plasma K2EDTA (0–10 ng/mL) no different false positives have been noticed. These outcomes may point out that plasma K2EDTA is accountable for non-specific binding however may equally be associated to variabilities from the individual donor samples. It has been reported that venom concentrations in human samples vary from < 1–1000 ng/mL within the first 30 h post-viper chunk, and from 10 to 100 ng/mL inside the first 10 h30. Based on these concentrations, the LFA could be most useful within the first 10 h following envenoming.
In comparability, LoDs of 10 ng/mL have been reached for B. atrox and L. muta spiked urine, with no false positives in clean urine. The total sign depth in spiked urine was similar to the sign depth in spiked working buffer. Still, this examine used pooled urine, and it’s understood that pooled samples have fewer dangers by way of matrix results26. It is anticipated that urine from individual donors would introduce higher uncertainty. The usefulness of urine for real-time monitoring of venom concentrations is unclear however urine is promising as a non-invasive matrix for reaching the ‘ease of sample collection’ intention of the (RE)ASSURED standards.
Troubleshooting matrix results in spiked serum
The LFA was examined in three completely different dilutions of clean sera (clotted blood and heat-inactivated) in working buffer (diluted 10×, 20×, and 100×), as it’s understood that matrix results may be lowered by diluting the matrix in buffer47. In each clean serum matrices, the ten× dilution resulted within the look of each check traces. In distinction, the 20× dilution solely prompted sign growth on the Lachesis traces, demonstrating {that a} bigger dilution within the working buffer lowered the sera matrix results. Testing the 100× diluted sera gave true destructive outcomes, indicating {that a} 1:99 µL dilution in working buffer may remove the undesirable matrix results in sera (SI Fig. S7).
The 1:99 ratio eradicated the false optimistic indicators (Fig. 4), but in addition led to a lot weaker check line sign intensities, leading to decrease T/C values, and better %RSDs than different matrices that used a ten:90 ratio (Table 2). Still, these have been foreseeable penalties because the venom focus within the serum was additionally diluted 100x, lowering the quantity of antigen available to bind on the check line. The LFAs examined in serum from clotted blood (Fig. 4a–c) had visible LoDs of 100 ng/mL and 50 ng/mL for B. atrox and L. muta venom, respectively. In distinction, the visible LoD within the heat-inactivated serum (Fig. 4a, d, e), was 500 ng/mL for each venoms. These LoDs are nonetheless inside the clinically related focus vary following viper chunk (< 1–1000 ng/mL)30 however would fall wanting detecting venoms on the decrease finish of this vary. Based on the extra pronounced matrix results and better LoDs in sera, it appears plasma or urine could be the popular matrices for the present LFA. Still, as talked about, a better pattern dilution was required to remove the matrix results in sera; the venom-spiked sera wanted to be diluted by an element of 100 with working buffer, leading to an efficient decrease venom focus in contrast with the experiments in different matrices. Therefore, the precise concentrations of venom detected within the experiments with serum have been 100× decrease than the LoDs reported right here (Table 2).
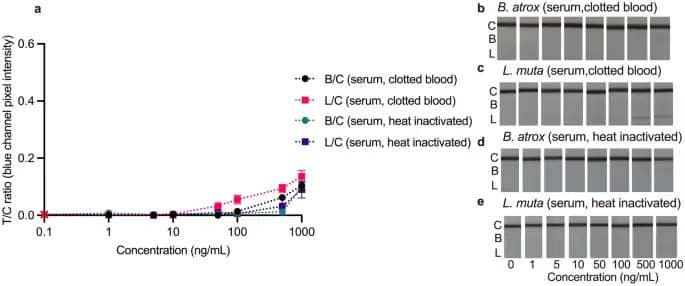
Calibration curves (a) and smartphone pictures (b–e) of the multiplex LFA examined in growing concentrations (1–1000 ng/mL) of B. atrox (b, d) and L. muta (c, e) spiked serum (1 µL spiked serum: 99 µL working buffer). Calibration curves are plotted as check traces divided by management traces (T/C) ratios (Bothrops/management = B/C; Lachesis/management = L/C) towards focus. The B/C isn’t proven for the L. muta assessments, and the L/C isn’t proven for the B. atrox assessments, as no indicators developed. Error bars symbolize the usual deviation (n = 3), and the crimson cross represents the sign in clean working buffer.
Evaluation of matrix results and non-specific binding
Antibodies are necessary for assay selectivity however should not infallible and may be topic to non-specific interactions26. To perceive the affect of non-specific binding on assay efficiency it is very important consider assays in clean matrices. The LFA was examined throughout repeat (n = 20) clean measurements in working buffer and the six individual organic matrices (n = 140) to guage the affect of pattern matrix on the assay (Fig. 5a). Matrix results can affect the analytical efficiency of an assay in two methods: (1) by growing non-specific binding resulting in a rise in sign depth in a destructive pattern, and (2) by influencing the precise binding thereby altering the sign depth in a optimistic pattern. Only two LFAs out of the 140 examined in clean matrices gave a weak sign on the Lachesis line; each these false positives occurred in plasma K2EDTA. While the check line indicators in these blanks have been extraordinarily weak, additional assay optimization could be wanted to remove them.
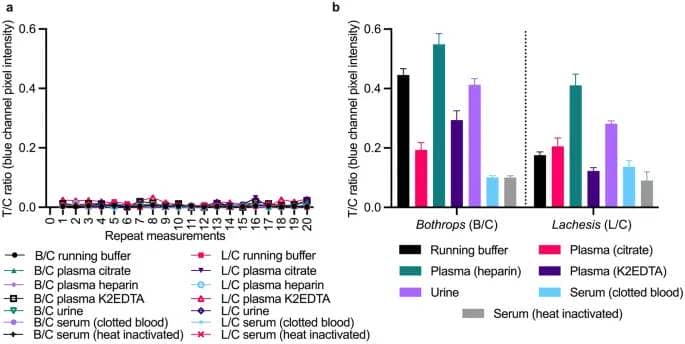
Matrix results in (a) clean pattern matrices (n = 20/matrix) and (b) at 1000 ng/mL of B. atrox or L. muta venom spiked into the matrices, plotted because the check line divided by management line (T/C) ratios (Bothrops/management = B/C; Lachesis/management = L/C) towards repeat measurements (a), or matrices (b). Error bars (b) symbolize the usual deviation (n = 3).
No different clean pattern matrix prompted the looks of check line indicators, demonstrating that the present working buffer composition and sample-to-running buffer ratios (10:90 and 1:99, respectively) have been acceptable for eliminating the prevalence of false positives within the examined matrices.
To additional perceive the affect of the pattern matrix on the LFA, B/C and L/C ratios (n = 3) have been plotted for every pattern matrix spiked with 1000 ng/mL of venom (Fig. 5b). Both the B/C and L/C ratios have been larger in spiked plasma heparin in contrast with spiked working buffer, suggesting that the pattern matrix influences the sign growth. Likewise, the L/C was larger in plasma citrate and urine in contrast with the working buffer. In comparability, these identical matrices yielded a decrease B/C, demonstrating that matrix sort influenced the check traces’ growth in a different way. This affect may very well be on account of interference from the anticoagulant used within the tube for storing the pattern or as a result of the samples are from individual donors. More samples from individual donors needs to be examined to higher perceive the extent of the matrix results on the LFA. Parameters associated to the analytical efficiency of the LFA are summarized in Table 2.
Assessing the affect of excessive antigen focus
Within a sandwich LFA’s dynamic working vary, the check line depth will increase with growing antigen concentrations, akin to an growing T/C ratio (Fig. 6). However, at concentrations above this vary, the check line depth (and T/C ratio) begins to lower, resulting in falsely low outcomes. At extra concentrations, the hook impact can happen, the place each the check line antibodies and the detection antibodies can grow to be saturated with antigen, stopping binding of the detection antibody on the check line40. These results happen at completely different concentrations relying on the precise assay and situations examined.
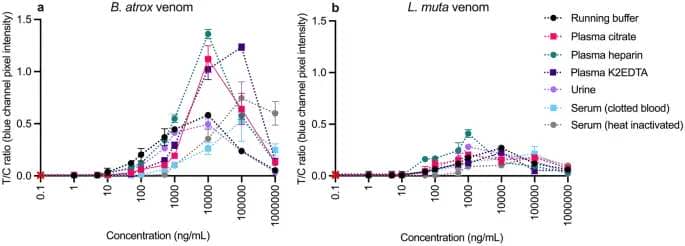
Multiplex LFA examined in an prolonged excessive antigen focus vary (1–1,000,000 ng/mL) in all pattern matrices. Calibration curves plotted as check line divided by management line (T/C) ratios (Bothrops/management = B/C; Lachesis/management = L/C) towards B. atrox (a) or L. muta, (b) venom concentrations. Error bars symbolize the usual deviation (n = 3 for 0–1000 ng/mL; n = 2 for 10,000–1,000,000 ng/mL), and the crimson cross represents the sign in a clean.
The Bothrops line sign depth and corresponding B/C ratio decreased at concentrations above 10,000 ng/mL in working buffer, plasma (citrate, heparin), and urine, or above 100,000 ng/mL in plasma (K2EDTA) and each sera (Fig. 6a). In distinction, the Lachesis line’s depth decreased at concentrations above 1000 ng/mL in plasma (citrate, heparin) and urine, above 10,000 ng/mL in working buffer and plasma K2EDTA, and above 100,000 ng/mL in each sera (Fig. 6b). It is logical that the lack of check line occurred at larger antigen concentrations in sera as these have been 10× extra diluted than the opposite matrices. In all matrices, optimistic check line indicators have been nonetheless seen at 1,000,000 ng/mL, though the intensities of those indicators have been weak and indistinguishable from these at a lot decrease concentrations (SI Fig. S8). In addition to inflicting a discount in sign depth, the excessive antigen concentrations additionally prompted a delay within the sign growth time, with indicators on the highest concentrations solely beginning to develop after 10 min.
Based on the literature it’s unlikely that the venom concentrations in bodily fluids could be excessive sufficient to trigger the hook impact30 within the developed assay. However, it has been reported that venom concentrations are larger in wound exudate or blister samples48. It is feasible that venom concentrations at a chunk web site may very well be excessive sufficient to trigger the hook impact. Therefore, appreciable testing with wound swabs could be required earlier than together with this as a possible pattern matrix.
Importantly, no sign developed on the Bothrops line in an extra of L. muta venom, or vice versa in any of the examined matrices, even at these excessive concentrations, indicating the usefulness of the LFA for differentiating between these venoms throughout a large focus vary.
Smartphone-based biosensor potential
Smartphones, mixed with mechanisms to regulate lighting situations for standardizing picture seize, have emerged as a well-liked software for buying and processing uncooked knowledge from optical measurements, resembling sign intensities from LFAs that may be correlated with antigen concentrations24. The LFA outcomes have been extra readable by the bare eye than by smartphone, however visible readout is subjective and untrained customers might misread ambiguous outcomes. Here, the smartphone was used solely to file knowledge to be analyzed in ImageJ. However, a future enchancment may very well be implementing on-smartphone processing, for real-time outcome interpretation and transmission to related healthcare personnel or storage in medical data, thereby, working in the direction of the (RE)ASSURED standards.



